As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Have you ever wondered what lies beneath the surface of the small animals you see every day? Their skulls hold secrets about how they live, eat, and survive.
Understanding common small animal skulls can give you a fascinating glimpse into their world. Whether you’re curious about pets, wildlife, or just love nature, knowing these skulls can change the way you see these creatures. Keep reading, and you’ll discover surprising facts that will make you look twice the next time you spot a tiny animal nearby.
Credit: www.wildlifetrusts.org
Skull Anatomy Basics
The skull is a vital part of small animals. It protects the brain and supports the face. Understanding skull anatomy helps identify different animals. It also shows how they live and eat.
Small animal skulls have many parts. Each part has a job. Some parts hold teeth. Others protect the brain or support the eyes. Learning these basics helps with animal study and care.
Key Skull Features
The skull has several key parts. The cranium holds the brain. The jaws carry teeth used for eating. Eye sockets protect the eyes. Nasal bones support the nose. These parts vary by animal type.
Differences Between Mammal Skulls
Mammal skulls differ in size and shape. Carnivores have sharp teeth for tearing meat. Herbivores have flat teeth for grinding plants. Rodents have large front teeth that keep growing. These differences show how animals survive.
Common Terms To Know
Some terms help describe skulls clearly. The mandible is the lower jaw. The maxilla is the upper jaw. Zygomatic arches form the cheekbones. Sutures are the joints between skull bones. Knowing these terms aids understanding and discussion.

Credit: charge.wisc.edu
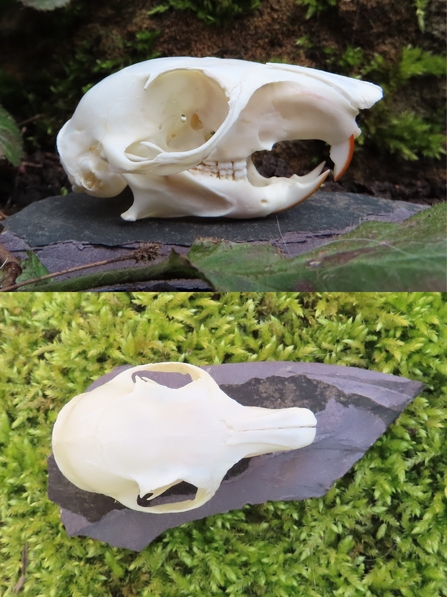
Rodent Skulls
Rodent skulls reveal much about these small animals. They share common features but also show unique traits. These skulls help identify species and understand their habits.
Characteristics Of Rat Skulls
Rat skulls are medium-sized and robust. Their incisors are large and curved, perfect for gnawing. The skull has a broad, flat shape. The eye sockets are relatively small. The nasal bones are long and narrow. Rats have strong jaw muscles, seen in wide cheekbones.
Mouse Skull Identification
Mouse skulls are smaller and more delicate than rats. Their noses are pointed and narrow. Incisors are sharp but smaller than rats’. Eye sockets are larger relative to skull size. The skull is lightly built with thin bones. Mice skulls show less muscle attachment compared to rats. The overall shape is more rounded.
Squirrel Skull Traits
Squirrel skulls are larger and more elongated. Their incisors are strong and curved for cracking nuts. The skull has a prominent ridge for muscle attachment. Eye sockets are large to support good vision. Squirrels have a distinct nasal bone shape. Their cheekbones are strong and wide. These traits help squirrels climb and forage.
Lagomorph Skulls
Lagomorph skulls belong to a group of small mammals that include rabbits and hares. These skulls have unique traits that help them survive in the wild. They show clear signs of their herbivore diet and fast movements. Understanding these skulls helps identify species and learn about their habits.
Rabbit Skull Features
Rabbit skulls are small and rounded. They have large eye sockets for wide vision. Their front teeth are sharp and keep growing. Behind these are smaller peg-like teeth. This helps rabbits chew tough plants. The skull has a strong jaw to support chewing. The nasal bones are long, aiding their keen sense of smell. The overall shape is compact, fitting their burrowing lifestyle.
Hare Skull Differences
Hare skulls are larger and more elongated than rabbits. Their eye sockets are bigger, giving better side vision. Their teeth are stronger for tougher vegetation. The jaw is more robust for powerful bites. The nasal bones are longer, which helps detect predators. Hare skulls have a lighter structure for quick running. These differences reflect hares’ need for speed and alertness.
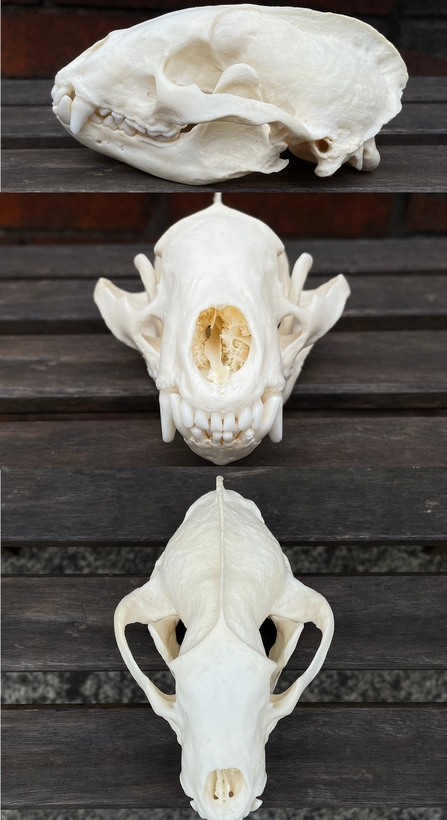
Small Carnivore Skulls
Small carnivore skulls show unique shapes and features. These skulls belong to animals that hunt small prey. Their bones reveal how they catch and eat food. Studying these skulls helps understand their behavior and biology.
Ferret Skull Overview
The ferret skull is long and narrow. It has sharp teeth for biting and tearing. Its large eye sockets suggest good vision. The skull is light but strong to support quick movements. Ferrets have well-developed jaws for hunting small animals.
Weasel And Mink Skull Traits
Weasel and mink skulls are similar but differ slightly in size. Both have pointed snouts and sharp teeth. Their skulls are compact with strong jaw muscles. These features help them kill prey quickly. Mink skulls are usually bigger with more robust teeth.
Skunk Skull Characteristics
Skunk skulls are broader than those of weasels and ferrets. They have a short snout and strong jawbones. Their teeth are less sharp but good for chewing plants and small animals. Skunks have a sturdy skull to protect against predators.
Small Herbivore Skulls
Small herbivore skulls show unique shapes and features. These animals have teeth made for chewing plants. Their skulls help protect their brains and support their chewing muscles. Learning about these skulls gives insight into their habits and needs.
Guinea Pig Skull Details
The guinea pig skull is round and compact. It has large eye sockets that help with wide vision. The front teeth grow continuously. They use these teeth to chew tough plants. The skull has strong jaw muscles for grinding food. The nasal bones are short, allowing a good sense of smell.
Chinchilla Skull Features
Chinchilla skulls are light but strong. Their teeth also grow all the time. The large cheekbones support strong chewing muscles. The eye sockets are big for sharp vision in low light. Their skull shape helps protect their delicate brain. The jaw joint allows side-to-side movement for grinding plants.

Credit: www.wildlifetrusts.org
Bird Skull Basics
Bird skulls are unique and fascinating. They differ from mammals and reptiles in many ways. Their shape and features help birds survive in different environments. Understanding bird skulls helps identify bird species and their habits.
Bird skulls are lightweight but strong. They have large eye sockets to support excellent vision. The beak replaces teeth and varies widely among species. These differences tell us what birds eat and how they live.
Common Bird Skull Traits
Most bird skulls share some traits. They have thin, hollow bones to reduce weight for flight. The braincase is large compared to body size. This supports their keen senses and quick reflexes.
The beak shape is a key trait. It suits the bird’s diet, such as seeds, insects, or fish. Eye sockets are positioned to give wide vision or depth perception. The skull bones fuse as birds grow, making the skull rigid.
Small Bird Skull Identification
Small bird skulls are harder to identify. Their tiny size means less detail is visible. Look for beak shape and size first. A thin, pointed beak often means insect eater. A short, thick beak points to seed eaters.
Check the size of the eye sockets. Large sockets may belong to nocturnal birds. The shape of the skull’s back can hint at the species group. Comparing these features helps match skulls to birds.
Using Skull Features For Identification
Identifying small animal skulls relies heavily on their unique features. Skulls hold clues to an animal’s diet, habits, and species. Observing key parts can help distinguish one skull from another quickly. This section highlights important features used in skull identification.
Teeth Patterns And Types
Teeth reveal much about an animal’s lifestyle. Herbivores have flat, broad teeth for grinding plants. Carnivores show sharp, pointed teeth for tearing meat. Omnivores display a mix of both types. The number and arrangement of teeth also vary by species. Noticing these patterns helps identify the animal’s diet and group.
Eye Socket Size And Placement
Eye sockets indicate vision and behavior. Large sockets suggest good night vision or a predator’s need to spot prey. Small sockets often belong to prey animals with wide vision. The position of the sockets on the skull matters. Forward-facing eyes imply depth perception for hunting. Side-placed eyes offer a wide field of view for spotting danger.
Nasal Cavity And Jaw Structure
The nasal cavity size shows an animal’s sense of smell. Larger cavities usually mean a strong smell sense. Jaw shape and strength tell about the bite force and diet. A strong jaw with large muscles suits meat-eaters. A lighter jaw fits herbivores that chew plants. These features together help identify the species and habits.
Tools And Techniques
Studying small animal skulls requires specific tools and techniques. These help identify species and understand anatomy accurately. Clear methods improve learning and make comparisons easier.
Measuring Skulls
Use calipers or rulers to measure skull length and width. Measure key parts like the jaw, eye sockets, and teeth spacing. Record measurements carefully for later analysis. Accurate measurements help distinguish between similar species.
Photographic References
Take clear photos from different angles. Use good lighting and a plain background. Include a scale or ruler in each photo. Photos allow detailed study without handling the skull repeatedly. They also help share findings with others.
Reference Guides And Resources
Use books and online databases with skull images and descriptions. Choose guides focused on small mammals or specific groups. These resources provide comparison charts and identification keys. Reliable references support correct identification and learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Most Common Small Animal Skulls Found?
Common small animal skulls include rodents, rabbits, squirrels, and small carnivores like weasels.
How Can You Identify Different Small Animal Skulls?
Look at teeth shape, size, and skull structure to tell species apart easily.
Why Study Small Animal Skulls Important?
Studying skulls helps understand animal diet, behavior, and evolution over time.
What Features Distinguish Rodent Skulls From Others?
Rodent skulls have large, sharp front teeth used for gnawing wood and plants.
How Do Carnivore Skulls Differ From Herbivore Skulls?
Carnivores have sharp teeth for tearing meat; herbivores have flat teeth for grinding plants.
Where Can I Find Small Animal Skulls For Study?
Skulls can be found in nature, museums, educational kits, or online stores.
Conclusion
Small animal skulls show many shapes and sizes. Each type tells a story about the animal’s life. Studying these skulls helps us learn about nature and animals. They reveal how animals eat, move, and live. Knowing common skull types makes identification easier.
This knowledge adds fun to your animal study. Keep exploring to discover more about these fascinating bones. Small animal skulls offer a window into the animal world.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.


