As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
If you love horses or want to learn more about these incredible animals, a Horse Anatomy Poster is a must-have for your space. Imagine having a clear, detailed guide right in front of you that shows every muscle, bone, and organ of a horse.
This simple tool can help you understand your horse better, care for it more effectively, and even impress others with your knowledge. Keep reading to discover why a Horse Anatomy Poster is more than just a picture—it’s your key to unlocking deeper insight into your favorite animal.
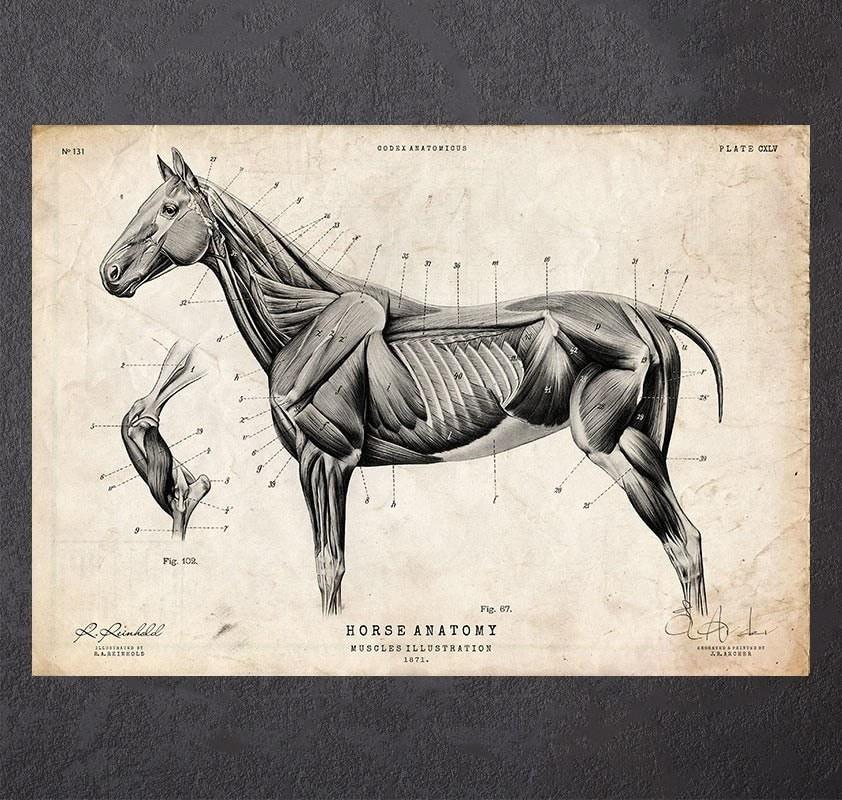
Credit: codexanatomy.com
Key External Features
Understanding the key external features of a horse helps in identifying and appreciating this majestic animal. These features are important for horse lovers, riders, and anyone curious about horses. A horse anatomy poster highlights these parts clearly. It shows the head, neck, legs, tail, and more. Each part has a specific function and appearance. Let’s explore the main external features.
Head And Facial Structure
The horse’s head is long and elegant. It holds the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. Large eyes give a wide field of vision. Ears move to catch sounds. The nostrils are wide for breathing. The mouth is used for eating and communication. The shape of the head varies by breed.
Neck And Shoulders
The neck connects the head to the body. It is strong and flexible. A well-shaped neck helps balance the horse. The shoulders are muscular and slope gently. They allow smooth movement. Good shoulder angle helps with speed and jumping.
Legs And Hooves
Horse legs are slender but powerful. They support the horse’s weight and allow fast running. The front legs carry most weight. The hooves are hard and protect the feet. Each hoof has a frog, sole, and wall. Proper hoof care is essential for horse health.
Tail And Mane
The tail is long and flowing. It helps with balance and keeps insects away. The mane runs along the neck’s top. It protects the neck from sun and rain. Both tail and mane vary in color and length by breed.
Skeletal System
The skeletal system is the strong frame of the horse’s body. It supports muscles and organs. It also protects vital parts like the heart and lungs. This system helps horses move with power and grace. Understanding the skeletal system is key to learning about horse health.
Major Bones
Horses have over 200 bones in their bodies. The skull protects the brain and supports the face. The spine runs from the neck to the tail. The legs have long bones like the femur and tibia. These bones are important for movement and strength. The pelvis connects the spine to the hind legs.
Joint Types
Joints connect bones and allow movement. Horses have several joint types. The hinge joint lets legs bend like a door. The ball-and-socket joint allows more rotation, found in the hip. Gliding joints in the spine let small movements between vertebrae. Healthy joints are vital for smooth, pain-free motion.
Spine And Ribcage
The spine supports the body and protects the spinal cord. It is made of many small bones called vertebrae. The ribcage protects the heart and lungs. Ribs connect to the spine and curve around the body. A strong spine and ribcage help horses carry weight and breathe easily.
Muscular System
The muscular system of a horse is vital for movement and strength. It helps horses run, jump, and carry loads. Muscles work by contracting and relaxing to create motion. Understanding this system aids in better horse care and training. A detailed horse anatomy poster shows these muscles clearly.
Primary Muscle Groups
Horses have several main muscle groups. The largest are the gluteal muscles in the hindquarters. These provide power for running and jumping. The forelimb muscles help with steering and balance. Neck muscles support the head and assist breathing. Back muscles maintain posture and support the rider’s weight.
Muscle Functions
Muscles control all horse movements. Some muscles help with speed and strength. Others assist in fine movements like lifting the head. Muscles also protect bones and joints. They store energy and help maintain body temperature. Proper muscle function is key to a healthy horse.
Common Muscle Injuries
Muscle injuries in horses often occur during exercise. Strains and tears are common. These cause swelling and pain. Overworking muscles can lead to fatigue and stiffness. Some injuries heal with rest and treatment. Early detection helps prevent long-term damage.

Credit: inkymousestudios.com
Circulatory And Respiratory Systems
The circulatory and respiratory systems are vital for a horse’s health. They work together to supply oxygen and nutrients to the body. The heart pumps blood while the lungs bring in oxygen. Understanding these systems helps in caring for horses better. A detailed horse anatomy poster shows these systems clearly.
Heart And Blood Flow
The horse’s heart is strong and large. It pumps blood throughout the body. Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to muscles and organs. The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. Blood flows from the heart to the lungs and back. This cycle keeps the horse active and healthy.
Lungs And Breathing
Horses have large lungs to take in oxygen. Breathing brings fresh air into the lungs. Oxygen passes into the blood here. Carbon dioxide leaves the blood and is exhaled. Breathing rate changes with exercise and rest. Healthy lungs help the horse perform well.
Signs Of Healthy Circulation
A strong pulse shows good heart function. Warm, pink gums indicate good blood flow. Normal breathing is calm and steady. The horse moves without stiffness or weakness. These signs mean the circulatory system works well.
Digestive System
The digestive system of a horse is complex and vital for its health. It helps the horse turn food into energy and nutrients. Understanding this system is important for anyone caring for horses. A detailed horse anatomy poster can show each part clearly. This section explains how food travels through the horse’s digestive tract and how nutrients are absorbed.
Mouth To Stomach
Digestion starts in the mouth. The horse uses its teeth to chew and break down food. Saliva mixes with the food to make swallowing easier. The food then moves down the esophagus to the stomach. The stomach is small but strong. It begins to break down food with acids and enzymes.
Intestinal Process
After the stomach, food enters the small intestine. This is where most digestion happens. Enzymes break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. The food then moves to the large intestine. Here, bacteria help digest fiber. This process produces essential nutrients for the horse.
Nutrient Absorption
Nutrients pass through the walls of the intestines into the bloodstream. This is how the horse gets energy and vitamins. The large intestine absorbs water to keep the horse hydrated. Proper nutrient absorption is key for the horse’s growth and health.
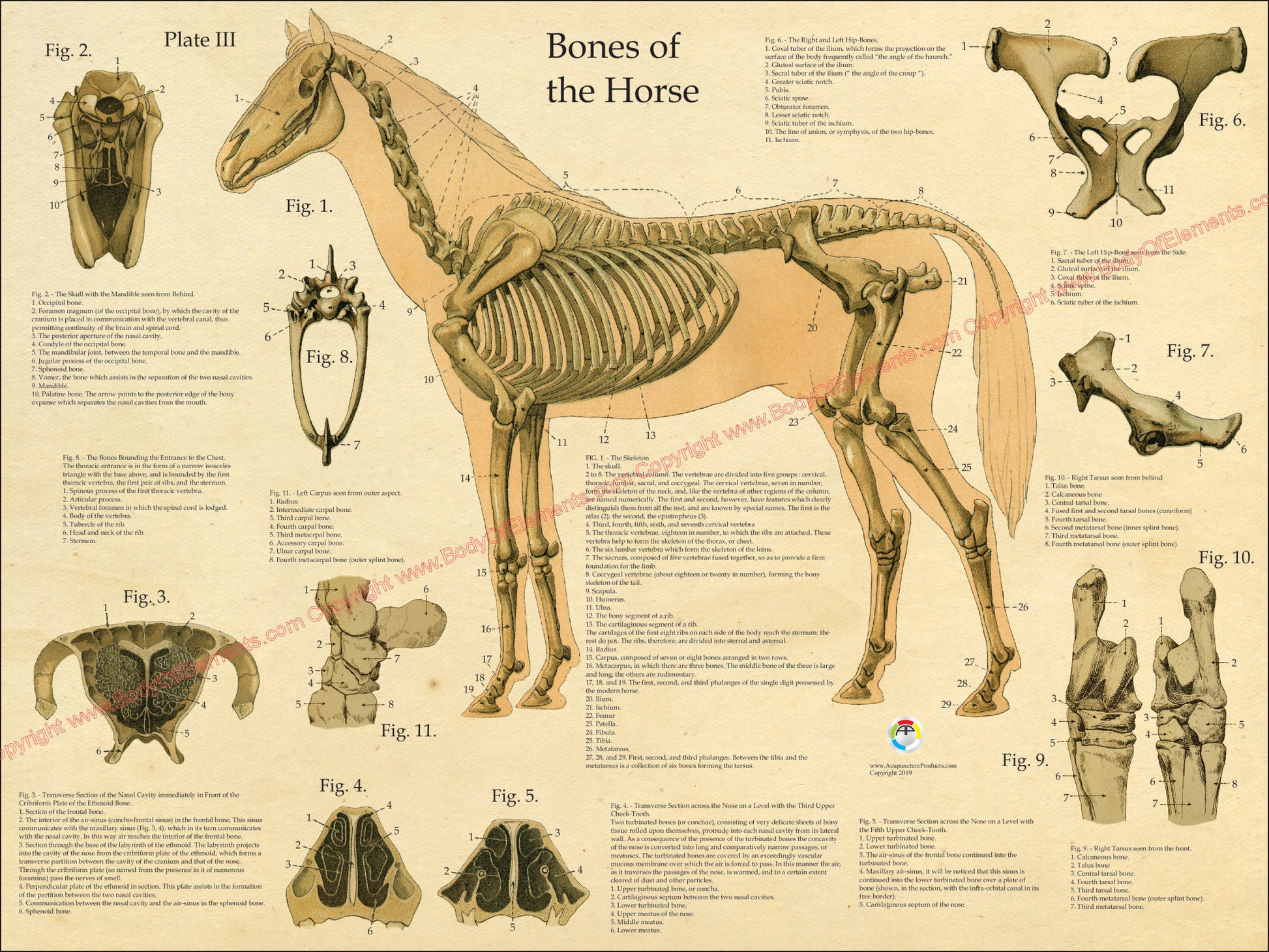
Credit: bodyofelements.com
Nervous System
The nervous system controls all the actions and reactions of a horse. It helps the horse move, feel, and respond to the environment. This system is very important for the horse’s survival and daily activities. Understanding the nervous system on a horse anatomy poster shows how complex and precise these functions are.
Brain And Spinal Cord
The brain is the control center of the nervous system. It processes information and sends commands to the body. The spinal cord connects the brain to the rest of the body. It carries messages back and forth quickly. Together, the brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system.
Nerve Functions
Nerves are like communication lines. They carry signals from the brain to muscles and organs. Nerves also send messages from the body back to the brain. This allows the horse to react to pain, touch, and temperature. Different nerves have specific jobs to keep the horse safe and active.
Sensory Organs
Sensory organs collect information from the environment. The eyes, ears, nose, and skin all work as sensors. They detect light, sound, smells, and touch. These organs send signals to the brain to help the horse understand its surroundings. Sensory organs are vital for a horse’s awareness and survival.
Reproductive Anatomy
The reproductive anatomy of horses is important for breeders and veterinarians. It helps to understand how horses reproduce and stay healthy. A horse anatomy poster often shows detailed parts of male and female reproductive systems. This section explains key structures and the reproductive cycle.
Male Structures
Male horses have several key reproductive parts. The testes produce sperm and hormones. The epididymis stores and matures sperm. The vas deferens transports sperm to the urethra. The penis delivers sperm during mating. The accessory glands add fluids to sperm, creating semen.
Female Structures
Female horses have ovaries that produce eggs. The fallopian tubes carry eggs to the uterus. The uterus supports the growing fetus. The cervix is the passage between uterus and vagina. The vagina is the birth canal and receives sperm. These parts work together for reproduction.
Reproductive Cycle
The reproductive cycle in female horses is called the estrous cycle. It lasts about 21 days. The cycle has phases: estrus, diestrus, and anestrus. Estrus is when the mare is fertile and can conceive. Hormones control these phases and prepare the body for pregnancy.
Creating Effective Posters
Creating effective horse anatomy posters requires clear visuals and easy-to-read information. The goal is to help viewers understand the horse’s body quickly. Good design makes learning simple and fun. Focus on clarity and neatness to keep attention.
Design Tips
Choose a clean layout with enough white space. Avoid clutter to help viewers focus. Use large, readable fonts for all text. Place the horse image in the center or on one side. Keep the background plain to highlight the main content.
Color Coding
Use different colors to separate body parts. This helps viewers see connections easily. Choose colors that contrast but do not hurt the eyes. Use a consistent color scheme across the poster. Explain the colors clearly in a small legend or key.
Labeling Techniques
Label parts with short, clear names. Use lines or arrows to connect labels to parts. Place labels close to the body part without covering important details. Use bold text for main parts and smaller text for details. Keep labels simple to avoid confusion.
Using Posters In Education
Using posters in education makes learning clear and fun. Visual aids help students see and remember important facts. A horse anatomy poster shows parts of the horse in detail. This can help learners understand the animal better and faster.
Classroom Activities
Teachers use horse anatomy posters for many activities. Students can label parts of the horse on the poster. Group discussions become easier with a clear visual. It helps students ask questions and share ideas. Posters make lessons more active and less boring.
Training Aid
Horse anatomy posters support training for riders and caretakers. They show muscles, bones, and organs clearly. Trainers use the posters to explain care and riding techniques. This helps learners see what happens inside the horse’s body. It improves their skills and safety.
Interactive Learning
Posters invite students to touch and explore. They can point to parts while the teacher explains. This hands-on approach helps memory and focus. Interactive learning with posters helps students connect words to images. It makes understanding horse anatomy easier and more fun.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Key Parts Are Shown On A Horse Anatomy Poster?
A horse anatomy poster shows bones, muscles, organs, and joints clearly.
How Can A Horse Anatomy Poster Help Beginners Learn?
It helps beginners by showing horse body parts in a simple, visual way.
Why Is Understanding Horse Anatomy Important For Riders?
Knowing horse anatomy helps riders care for horses and avoid injuries.
What Materials Are Best For Durable Horse Anatomy Posters?
Laminated paper or vinyl materials make horse anatomy posters long-lasting.
Can A Horse Anatomy Poster Help With Vet Visits?
Yes, it helps owners understand vet advice and spot health issues.
Where Should I Place A Horse Anatomy Poster For Best Use?
Place it in stables or tack rooms for easy, regular reference.
Conclusion
A horse anatomy poster helps you learn horse parts clearly. It shows bones, muscles, and organs in simple ways. Students, trainers, and horse lovers find it useful every day. Understanding horse body helps in better care and training. This visual guide makes learning fast and easy.
Keep one handy for quick reference anytime. It is a great tool to explore horse health and structure. A clear picture says more than many words.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.


