As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
If you want to truly understand horses, knowing their anatomy is a must. Whether you’re a rider, trainer, or just a horse lover, having a clear picture of your horse’s body helps you care for them better.
Imagine being able to spot signs of discomfort early or improving your riding by understanding how their muscles and bones work. This horse anatomy chart will give you an easy-to-follow guide that breaks down everything you need to know. Keep reading, and you’ll discover details that can make a real difference in your connection with horses.

Credit: sco.wikipedia.org
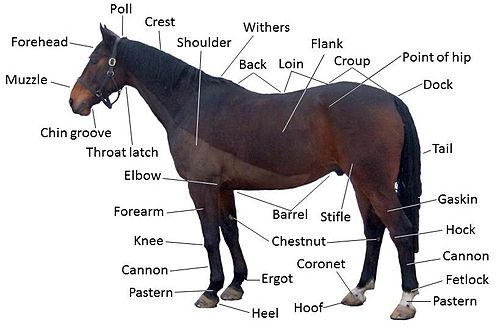
External Features
The external features of a horse show its strength and grace. These parts are easy to see and help the horse in many ways. Understanding these features helps you learn more about horses. Each part has a special role in the horse’s daily life and movement.
Head And Facial Parts
The horse’s head holds important parts like eyes, ears, and nostrils. Eyes help it see in wide angles. Ears turn to catch sounds around. Nostrils are large to breathe well during fast runs. The mouth has strong teeth to chew grass and hay.
Neck And Throat
The neck connects the head to the body. It is long and strong. The throat area lets air pass to the lungs. Muscles here help the horse raise or lower its head. The neck also helps balance the horse’s body.
Body And Barrel
The body holds the heart, lungs, and stomach. The barrel is the round part of the body. It stores food and water inside. The ribs protect the organs. The skin and coat cover the whole body to keep the horse warm or cool.
Legs And Hooves
Legs support the horse’s weight and allow movement. Strong bones and muscles help run fast or jump high. Hooves are hard and protect the feet. They absorb shock and provide traction on different grounds. Horses need good hoof care for health.
Tail And Mane
The tail helps the horse keep balance and shoo away insects. The mane grows along the neck. It adds protection against weather and bugs. Both tail and mane add to the horse’s beauty and style.
Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Skeletal Structure
The skeletal structure of a horse is its strong frame. It supports the body and protects vital organs. This structure helps horses move with grace and power. Understanding the bones helps in caring for horses better. The skeleton includes the skull, spine, ribs, chest, limbs, and joints.
Skull And Spine
The skull protects the horse’s brain and senses. It has many bones joined tightly together. The spine runs from the skull to the tail. It supports the body and allows flexibility. The spine has many small bones called vertebrae. These bones protect the spinal cord inside.
Ribs And Chest
The ribs form a cage around the horse’s chest. They protect the heart and lungs. There are 18 pairs of ribs in most horses. The chest is deep and wide to hold big lungs. Strong ribs help the horse breathe well during work.
Limbs And Joints
Horse limbs are long and strong for running and jumping. Each limb has bones connected by joints. Joints allow movement like bending and twisting. The front legs have shoulder, elbow, and knee joints. The back legs include hip, stifle, and hock joints. Healthy joints keep horses active and pain-free.
Muscular System
The muscular system of a horse plays a vital role in its movement and strength. It consists of many muscles working together to help the horse run, jump, and carry weight. Understanding this system helps in caring for the horse’s health and performance.
Major Muscle Groups
Horses have several major muscle groups that support different actions. The neck muscles help in head movement and balance. The shoulder muscles assist in forelimb movement. The back muscles provide support and power for the horse’s stride. The hindquarters contain large muscles that drive the horse forward.
Muscle Functions
Muscles contract to create movement. Some muscles help with fine motor control, like moving the ears. Others power big actions such as running or kicking. Muscles also maintain posture and absorb shock during movement. Strong muscles improve the horse’s agility and endurance.
Common Injuries
Muscle strains are common injuries in horses. Overuse or sudden movements can cause tears or soreness. Muscle cramps may occur due to dehydration or poor nutrition. Early treatment is important to avoid long-term damage. Rest and proper care help muscles heal faster.
Digestive System
The digestive system of a horse is complex and vital for its health. It breaks down food into nutrients and energy. Understanding this system helps in better care and feeding practices. The process starts in the mouth and continues through the stomach and intestines. Each part plays a unique role in digestion.
Mouth And Teeth
The mouth is the first step for food intake. Horses use their teeth to chew and grind food. Chewing breaks food into smaller pieces. This makes swallowing easier and aids digestion. Saliva mixes with food to start breaking it down. Teeth wear down over time and need checking by a vet.
Stomach And Intestines
The stomach holds food for a short time. It uses acids to break down food further. Horses have a small stomach compared to their body size. Food moves quickly into the intestines. The intestines absorb nutrients and water. The large intestine ferments fiber, helping digestion.
Nutrient Absorption
Nutrients pass through the intestines into the bloodstream. This process fuels the horse’s body and organs. Fiber digestion produces energy through fermentation. Water absorption keeps the horse hydrated. Poor absorption can cause health problems. Proper diet supports good nutrient absorption.
Respiratory System
The respiratory system in horses is vital for their survival and performance. It supplies oxygen to the body and removes carbon dioxide. Proper breathing supports energy and endurance during exercise. Understanding this system helps in caring for horses effectively.
Nasal Passages
The nasal passages are the first part of the horse’s airway. They warm and filter the air before it reaches the lungs. These passages also help the horse smell its environment. Their size and shape affect how easily the horse breathes.
Lungs And Airways
The lungs are the main organs for gas exchange. They contain tiny air sacs called alveoli. Oxygen passes from the alveoli into the blood. Airways, including the trachea and bronchi, carry air to the lungs. Any blockage here can cause breathing problems.
Breathing Mechanism
Horses breathe using muscles around their ribs and diaphragm. When these muscles contract, the chest expands and air flows in. Relaxing the muscles pushes air out. This rhythm keeps oxygen moving in and carbon dioxide moving out.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system in horses plays a vital role in keeping their bodies healthy. It moves blood, oxygen, and nutrients to all parts of the body. This system also helps remove waste from cells. Understanding the horse’s circulatory system is important for horse care and health.
Heart Anatomy
The horse’s heart is a strong muscle about the size of a basketball. It has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The heart pumps blood to the lungs and the rest of the body. A healthy heart keeps the horse active and full of energy.
Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are tubes that carry blood through the horse’s body. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart. Veins bring oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Capillaries connect arteries and veins and help deliver nutrients to cells.
Circulation Process
Blood flows from the heart to the lungs to pick up oxygen. Then, it moves back to the heart and gets pumped to the whole body. Cells use the oxygen and nutrients in the blood to work properly. Waste products from cells travel back in the blood to be removed.
Nervous System
The nervous system controls how a horse thinks, feels, and moves. It sends messages from the brain to the body. This system helps horses react quickly to their environment. It keeps them safe and aware of what happens around them.
Brain And Spinal Cord
The brain is the control center of the horse. It processes information and makes decisions. The spinal cord connects the brain to the rest of the body. It carries signals back and forth. Together, they coordinate movement and balance.
Nerves And Sensory Organs
Nerves are like wires that send messages through the body. Sensory organs, such as eyes and ears, detect the world. They send signals to the brain. These signals tell the horse about sounds, sights, and touch.
Reflexes And Responses
Reflexes are quick, automatic actions. They protect the horse from danger. For example, pulling away from something sharp. Responses involve more thinking. They allow horses to learn and adapt.

Credit: www.equishop.com
Reproductive System
The reproductive system of a horse plays a key role in the continuation of the species. It involves organs and structures that allow horses to reproduce and produce offspring. Understanding this system helps in caring for horses and managing breeding effectively.
Male Anatomy
The male horse’s reproductive system includes the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, and penis. The testes produce sperm and hormones like testosterone. The epididymis stores and matures sperm. The vas deferens carries sperm during ejaculation. The penis delivers sperm to the female during mating.
Female Anatomy
The female horse’s reproductive system has ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, and vagina. Ovaries release eggs and produce hormones like estrogen. Oviducts transport eggs to the uterus. The uterus supports the developing foal. The cervix controls entry to the uterus. The vagina serves as the birth canal and mating site.
Breeding Considerations
Timing is important in horse breeding. Mares have an estrous cycle lasting about 21 days. Ovulation happens near the cycle’s end. Breeders observe signs like behavior and physical changes. Proper nutrition and health care improve breeding success. Safe handling during mating reduces stress and injury risk.
Common Health Concerns
Understanding common health concerns in horses helps owners keep their animals safe. Horses rely on strong anatomy to stay active and healthy. Some health issues relate directly to their body structure. Recognizing these problems early can prevent serious conditions.
Anatomy-related Issues
Joint problems often affect horses, especially in knees and hocks. Arthritis can develop, causing pain and stiffness. Hoof diseases like laminitis damage the foot’s sensitive structures. Muscle strains and tendon injuries happen due to overwork or poor footing. Digestive issues, such as colic, relate to the horse’s gut anatomy and diet.
Preventative Care
Regular grooming checks for cuts, swelling, or lumps. Proper hoof care prevents many foot-related problems. Balanced nutrition supports strong bones and muscles. Exercise keeps joints flexible and muscles strong. Vaccinations and deworming reduce risks of infections and parasites.
When To Consult A Vet
Call a vet if the horse shows lameness or swelling. Sudden changes in eating or drinking habits need attention. Persistent coughing or difficulty breathing require immediate care. Signs of colic, such as rolling or pawing, are urgent. Early vet visits can save lives and reduce recovery time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Parts Shown In A Horse Anatomy Chart?
A horse anatomy chart shows the head, neck, body, legs, and hooves clearly.
Why Is Understanding Horse Anatomy Important For Riders?
Knowing horse anatomy helps riders care for horses and prevent injuries during riding.
How Does A Horse’s Skeletal System Support Its Movement?
The skeleton gives structure and support, allowing horses to run and jump smoothly.
What Muscles Are Key For A Horse’s Strength And Speed?
Leg and back muscles are crucial for power and fast movement in horses.
How Can A Horse Anatomy Chart Help In Spotting Health Issues?
It helps identify body parts and notice swelling, cuts, or abnormal shapes early.
Are Horse Anatomy Charts Useful For Beginners In Horse Care?
Yes, they make learning about horse body parts simple and improve horse handling skills.
Conclusion
Understanding the horse anatomy chart helps you care for horses better. It shows important parts like muscles, bones, and organs clearly. Knowing these parts makes it easier to spot health problems. This knowledge supports training, riding, and grooming safely. Keep studying the chart to deepen your horse care skills.
A strong foundation in anatomy benefits both you and the horse. Simple tools like this chart make learning quick and clear. Use it often to improve your connection with horses.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.


