As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Wondering how long it takes for testosterone to leave a neutered dog’s system? The answer is not immediate.
It usually takes a few weeks for testosterone levels to decrease significantly. Neutering your dog has many benefits, such as reducing aggression and preventing certain health issues. But understanding the timeline for hormonal changes can help you manage your dog’s behavior better.
After neutering, a dog’s testosterone levels gradually drop. This process varies depending on the dog’s age, breed, and health. Typically, testosterone decreases over a period of two to four weeks. During this time, you may still notice some hormonal behaviors. Patience and proper care will help your dog adjust to these changes. In this blog, we’ll explore the detailed timeline and what to expect during this transition period.
Introduction To Neutering
Neutering is a common procedure for dogs. It involves removing the testicles of male dogs. This reduces the amount of testosterone in their body.
Many pet owners have questions about neutering. They want to understand its purpose, benefits, and effects on their dog’s health.
Purpose And Benefits
Neutering has several important purposes and benefits:
- Population control: Neutering helps reduce the number of unwanted puppies.
- Health benefits: Neutering lowers the risk of certain cancers and infections.
- Behavioral improvements: It can reduce aggression, roaming, and marking behaviors.
Common Misconceptions
There are many misconceptions about neutering. Some people believe neutering will change their dog’s personality. This is not true. Neutering does not change a dog’s core personality.
Another misconception is that neutering causes weight gain. This is also false. Proper diet and exercise prevent weight gain, not the procedure itself.
Understanding these facts helps pet owners make informed decisions. It ensures the health and well-being of their furry friends.
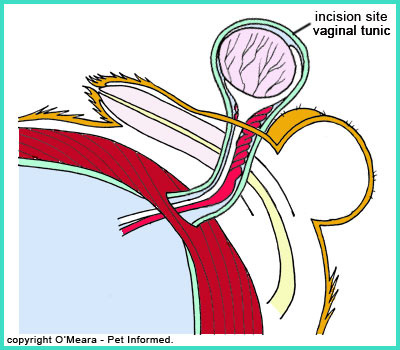
Credit: www.pet-informed-veterinary-advice-online.com
Testosterone In Dogs
Testosterone plays a crucial role in a dog’s life. This hormone affects physical development and behavior. Neutering a dog removes the primary source of testosterone. Understanding its effects is vital for dog owners.
Role Of Testosterone
Testosterone is produced in the testes. It is responsible for the development of male characteristics. These include muscle mass, bone density, and reproductive organs. The hormone also influences a dog’s energy levels.
Effects On Behavior
Testosterone affects a dog’s behavior significantly. It can lead to increased aggression and territorial marking. Dogs with high testosterone levels may show dominant behavior. They might also be more likely to roam.
After neutering, testosterone levels decrease. The change may take a few weeks to be noticeable. Behavior improvements can be observed over time.
Table Of Testosterone Reduction Timeline
| Time After Neutering | Testosterone Levels |
|---|---|
| Immediately | High |
| 1 Week | Moderate |
| 2-4 Weeks | Low |
| 4-6 Weeks | Minimal |
Understanding the role and effects of testosterone helps in managing your dog’s behavior post-neutering. Neutering brings several benefits. These include reduced aggression and less roaming. Patience is key as hormonal changes take time.
Post-neutering Hormonal Changes
Neutering a dog involves removing its testicles. This leads to significant hormonal changes. Testosterone levels drop, affecting behavior and physiology. These changes help reduce aggression and roaming tendencies. Understanding the timeline of these changes is crucial for pet owners.
Initial Hormonal Drop
The first change happens soon after neutering. Testosterone levels drop quickly. Within 24 to 48 hours, there is a significant decrease. Your dog might start to show calmer behavior. This rapid decline marks the beginning of the hormonal shift.
Gradual Decline Over Time
The decline continues over several weeks. Full hormonal stabilization can take up to six months. During this period, you may see gradual changes. Reduced aggression, less marking, and a calmer demeanor are common. Each dog is different, so the timeline can vary.

Credit: parkvet.net
Typical Timeline For Hormone Reduction
Neutering a dog has many benefits, including the reduction of testosterone levels. Understanding the timeline for hormone reduction helps manage expectations and care for your pet better.
First Few Days
In the first few days after neutering, testosterone levels start to decline. However, the hormone is not completely gone. The body needs time to adjust and eliminate the remaining testosterone.
During this period, you may still notice some typical male behaviors. Be patient. The body is just beginning the process of hormonal change.
One Week To One Month
By the end of the first week, you might see a noticeable drop in testosterone. Yet, it can take up to a month for the hormone to reduce significantly.
Studies show that testosterone levels continue to decline steadily over this period. Full behavioral changes may not be evident yet. The body needs time to fully adapt.
To summarize:
| Timeframe | Testosterone Levels |
|---|---|
| First Few Days | Start to decline |
| One Week | Noticeable drop |
| One Month | Significant reduction |
As testosterone decreases, you will likely observe fewer male-specific behaviors. Remember, each dog is unique. The timeframe can vary slightly.
Factors Influencing Hormone Levels
Understanding the factors influencing hormone levels after neutering is important. Testosterone levels in dogs can vary due to several reasons. The time it takes for testosterone to leave a dog’s system depends on these factors. Two primary factors to consider are the age at neutering and the individual health of the dog.
Age At Neutering
The age at which a dog is neutered plays a significant role. Younger dogs tend to have a quicker reduction in testosterone levels. In puppies, the hormone levels drop faster. In older dogs, the process may take longer. This is because their bodies have adjusted to higher testosterone levels. Therefore, age is a key factor in determining how quickly testosterone leaves the system.
Individual Health
Individual health is another critical factor. A dog’s overall health can affect hormone levels post-neutering. Healthier dogs may experience faster hormonal changes. Dogs with health issues might take longer to adjust. Weight, breed, and genetic factors also influence this process. Each dog is unique, and their hormone levels will adjust differently.
Behavioral Changes After Neutering
Neutering a dog can lead to various behavioral changes. These changes can occur both immediately and over a longer period. Understanding these changes helps in ensuring a smooth transition for your dog.
Immediate Effects
Right after neutering, you may notice some immediate effects on your dog’s behavior. These changes are often due to the sudden drop in testosterone levels.
- Calmer demeanor: Many dogs become less hyperactive soon after surgery.
- Reduced aggression: Aggressive tendencies often decrease within the first few days.
- Less roaming: The urge to wander in search of a mate diminishes quickly.
- Appetite changes: Some dogs experience a temporary change in their eating habits.
Long-term Adjustments
As weeks turn into months, dogs continue to adjust to the absence of testosterone. Long-term behavioral changes become more noticeable.
- Stable temperament: Dogs usually become more even-tempered over time.
- Improved focus: Training often becomes easier as dogs become less distracted.
- Fewer marking incidents: The urge to mark territory with urine significantly reduces.
- Better social interactions: Dogs tend to get along better with other pets.
Monitoring these changes can help ensure your dog remains happy and healthy. Understanding the timeline and nature of these behavioral changes is crucial for effective care.
Managing Post-neutering Care
Neutering your dog is an important step for their health and well-being. After the procedure, your dog will need special care to ensure a smooth recovery. This section will help you manage post-neutering care effectively, focusing on monitoring health and supporting recovery.
Monitoring Health
After neutering, it’s crucial to keep an eye on your dog’s health. Watch for any signs of infection or complications. Check the incision site daily. Look for redness, swelling, or discharge. If you see any of these signs, contact your vet immediately.
Keep track of your dog’s appetite and energy levels. A drop in either could signal a problem. Ensure your dog drinks plenty of water to stay hydrated. Monitor their bowel movements too. Any drastic changes might need a vet’s attention.
Here is a simple table to help you monitor your dog’s health:
| Health Aspect | What to Watch For |
|---|---|
| Incision Site | Redness, swelling, discharge |
| Appetite | Decrease in food intake |
| Energy Levels | Unusual lethargy |
| Hydration | Drinking less water |
| Bowel Movements | Changes in frequency or consistency |
Supporting Recovery
Your dog needs comfort and rest to recover. Create a quiet, comfortable space for them. Limit their physical activity to prevent strain on the incision site. Short, gentle walks are okay, but avoid running or jumping.
Ensure your dog wears an Elizabethan collar if needed. It will stop them from licking or biting the incision. This helps prevent infection and promotes healing.
Follow your vet’s instructions on medication and care. Administer prescribed pain relief as directed. Never give human painkillers to your dog.
Here are some tips to support your dog’s recovery:
- Provide a calm and quiet environment.
- Limit physical activity.
- Use an Elizabethan collar if necessary.
- Follow all vet instructions carefully.
- Keep an eye on your dog’s behavior and health.
By carefully monitoring health and supporting recovery, your dog will heal quickly and comfortably. Post-neutering care is crucial for their well-being.

Credit: dogo.app
Faqs On Neutering And Testosterone
Neutering a dog brings many questions. One key concern is testosterone levels. Below, we answer common questions. Learn from expert advice to understand what to expect.
Common Concerns
Many pet owners wonder, “How long after neutering is testosterone gone?” It’s a valid question. Testosterone affects behavior and health. Here are some common concerns:
- How fast will testosterone levels drop?
- Will my dog’s behavior change immediately?
- Can neutering affect my dog’s health?
- Is there a difference in neutering ages?
Testosterone levels start to decline right after neutering. It may take a few weeks for a significant drop. Most dogs see full changes in three to six weeks.
Expert Advice
Experts often recommend neutering at a young age. This can prevent unwanted behaviors linked to testosterone. But what do the experts say about the process?
- Behavioral Changes: After neutering, some dogs become calmer. Others may still have old habits for a while.
- Health Benefits: Neutering can reduce risks of certain cancers. It also decreases the chance of prostate problems.
- Timeframe: Experts suggest waiting at least six weeks to see full effects. This allows time for testosterone to leave the system.
Neutering brings many benefits. It helps with behavior and health. Most importantly, it ensures a better quality of life for your dog.
| Timeframe | Testosterone Level |
|---|---|
| 1 Week | High |
| 3 Weeks | Moderate |
| 6 Weeks | Low |
In summary, patience is key. Your dog’s testosterone levels will drop. Watch for changes over a few weeks. Consult your vet for personalized advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Testosterone Remain After Neutering?
After neutering, testosterone levels in dogs typically diminish within a few weeks. However, it can take up to six weeks for the hormone to completely leave the body.
When Will My Dog’s Behavior Change Post-neutering?
Behavioral changes in dogs post-neutering can begin within a few weeks. Complete behavioral adjustments may take several months.
Can Neutering Affect My Dog’s Energy Levels?
Yes, neutering can affect a dog’s energy levels. Typically, you may observe a decrease in hyperactive behaviors within a few weeks.
Does Neutering Immediately Stop Testosterone Production?
No, neutering does not immediately stop testosterone production. It gradually decreases over a few weeks until completely gone.
Conclusion
Understanding how long testosterone stays after neutering helps manage expectations. Typically, it takes several weeks for testosterone levels to drop. This timeline varies based on individual dogs. Observing behavior changes can offer clues. Patience and care are key during this period.
Consult your vet for personalized advice. They provide the best guidance and support. Your dog’s health is the top priority. With time and care, you will see positive changes. Neutering benefits your dog’s well-being and behavior.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

