As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
If you care for horses, understanding their health is a top priority. Hind gut ulcers in horses are a hidden problem that can cause your horse serious discomfort and affect their performance.
You might not see obvious signs right away, but these ulcers can quietly damage your horse’s digestive system. Knowing how to spot the symptoms and what steps to take can make all the difference in your horse’s well-being. Keep reading to discover what causes hind gut ulcers, how they impact your horse, and what you can do to help them feel their best.
Hind Gut Ulcers In Horses
Hind gut ulcers in horses are a common but often overlooked health issue. These ulcers form in the lower part of the horse’s digestive system. This area includes the cecum and large colon, where food is broken down and absorbed.
Ulcers in the hind gut can cause pain and discomfort. They may lead to changes in behavior and poor performance. Understanding this condition helps horse owners spot symptoms early and seek proper care.
What Are Hind Gut Ulcers?
Hind gut ulcers are sores in the lining of the horse’s large intestine. The hind gut is acidic and sensitive. Too much acid or poor diet can damage this area. Ulcers reduce the gut’s ability to absorb nutrients well.
Causes Of Hind Gut Ulcers
Diet plays a big role in causing ulcers. High grain intake and low fiber diets increase acid levels. Stress and illness can also harm the gut lining. Long-term use of some medications may worsen ulcers.
Signs And Symptoms
Signs can be subtle and hard to notice. Horses may show weight loss, poor appetite, or dull coat. Some become cranky or avoid work. Colic and diarrhea are possible signs too.
How To Diagnose Hind Gut Ulcers
Diagnosing is tricky because symptoms overlap with other issues. Vets often use blood tests and fecal exams. Gastroscopy does not show hind gut ulcers. Diagnosis relies on signs and ruling out other problems.
Treatment focuses on reducing acid and healing the gut. Special diets high in fiber help protect the gut lining. Some medications can reduce acid and support healing. Managing stress is important during recovery.
Common Causes
Hind gut ulcers in horses develop due to several common causes. These factors affect the stomach and intestines. Understanding these causes helps in preventing and managing ulcers effectively.
Diet And Feeding Habits
Feeding plays a big role in gut health. Horses eating large amounts of grain or rich feed often face higher ulcer risks. Lack of enough fiber slows digestion and harms the gut lining. Irregular feeding times upset the digestive system. Constant access to fresh forage supports healthy digestion.
Stress And Environment
Stress affects horses deeply. Changes in environment, transport, or stable routines cause stress. Horses under stress produce more stomach acid. This acid damages the gut lining and causes ulcers. Quiet and stable surroundings help reduce stress levels.
Medication Impact
Some medications harm the horse’s gut. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are common culprits. Long-term use of these medicines reduces protective mucus in the intestines. This leaves the gut vulnerable to ulcers. Always monitor medication use and consult a vet.
Exercise And Workload
Heavy exercise increases acid production in the stomach. Horses in intense work often develop ulcers. Lack of proper rest worsens the problem. Balanced exercise with rest days helps maintain gut health. Avoid sudden changes in workload to reduce risk.
Recognizing Symptoms
Hind gut ulcers in horses can be hard to spot at first. The symptoms are often subtle and easy to miss. Knowing what signs to watch for helps catch problems early. This can improve treatment results and keep horses healthy and happy.
Behavioral Changes
Horses with hind gut ulcers often act differently. They may seem more irritable or restless. Some horses stop wanting to be touched or groomed. Others may show signs of anxiety or avoid their usual routines. These changes can be the first clues of discomfort.
Digestive Signs
Ulcers in the hind gut affect digestion. Horses might have loose stools or diarrhea. Some may show signs of colic, such as pawing or rolling. Loss of appetite or slow eating can also occur. Watch for weight loss or poor coat condition as well.
Performance Issues
Ulcers can reduce a horse’s energy and stamina. They may tire quickly during exercise. Some horses resist work or seem less willing to perform. A drop in performance without injury can signal an ulcer problem. Trainers and riders should note these changes carefully.
Physical Indicators
Physical signs include sensitivity in the abdominal area. Horses might flinch or react when touched near the hind gut. Some develop a tucked-up belly or show muscle loss. Dull eyes and a lack of alertness are also common. These signs point to internal discomfort.
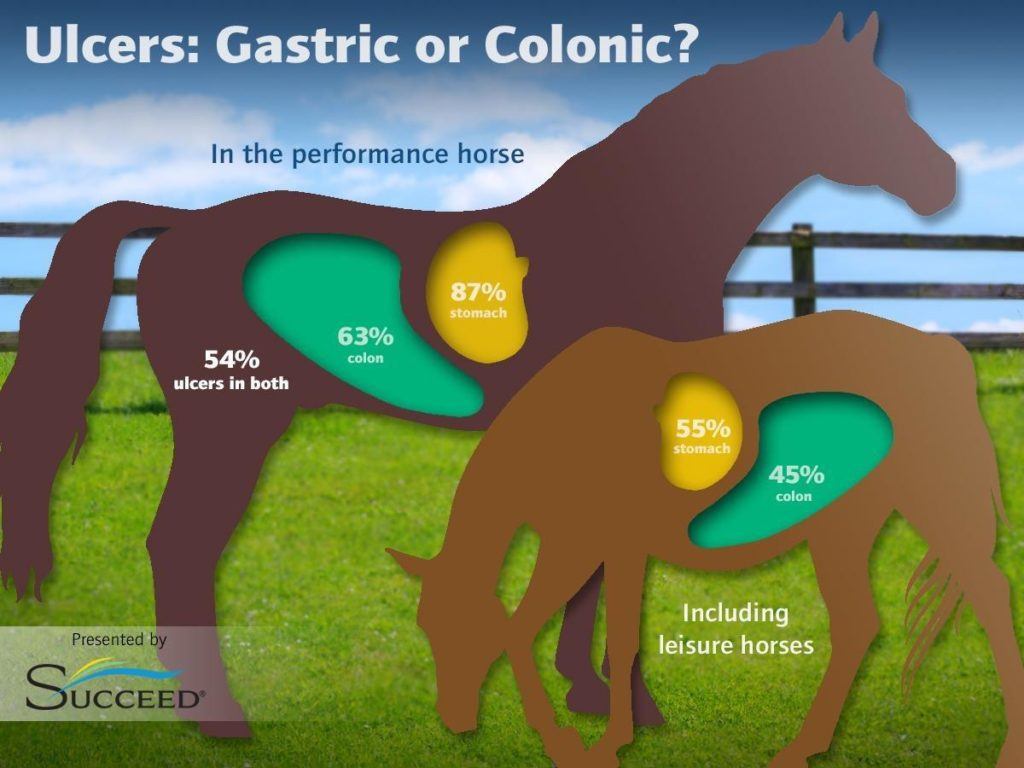
Credit: www.succeedfbt.com
Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosing hind gut ulcers in horses requires careful observation and several diagnostic methods. These methods help identify the problem accurately. Early diagnosis improves treatment success and horse health.
Veterinary Examination
A vet starts with a full physical check. They look for signs like weight loss, poor appetite, or changes in behavior. The vet also listens to the horse’s gut sounds. These clues guide further testing.
Endoscopy Procedures
Endoscopy uses a flexible camera to view inside the horse’s gut. It helps spot ulcers or inflammation in the hind gut. This method gives clear images for a precise diagnosis. Sedation is often needed to keep the horse calm.
Laboratory Tests
Lab tests analyze blood and feces samples. Blood tests check for anemia or infection signs. Fecal tests look for parasites or bacteria causing gut problems. These tests support the vet’s findings from exams and endoscopy.
Differential Diagnosis
Several conditions cause similar signs as hind gut ulcers. The vet rules out colic, gastritis, or infections. This step ensures the correct problem is treated. Accurate diagnosis avoids unnecessary treatments.
Treatment Options
Treating hind gut ulcers in horses requires a balanced approach. Careful management helps heal ulcers and prevents new ones. Different methods work together for better results.
Medications And Supplements
Vets often prescribe medications to reduce acid and heal ulcers. Some drugs protect the gut lining from damage. Supplements with fiber and probiotics support gut health. These help restore good bacteria in the hind gut.
Dietary Adjustments
Feeding changes reduce stress on the horse’s gut. More forage and less grain improve digestion. Small, frequent meals keep the gut stable. Adding fiber-rich feeds helps maintain a healthy gut environment.
Stress Management
Stress affects ulcer healing and gut health. Calm environments reduce stress hormones that harm the gut. Regular exercise and consistent routines help horses relax. Avoid sudden changes in work or living conditions.
Alternative Therapies
Some horse owners use herbal remedies to soothe ulcers. Natural anti-inflammatories may reduce gut irritation. Acupuncture can improve blood flow and healing. Always check with a vet before trying new therapies.
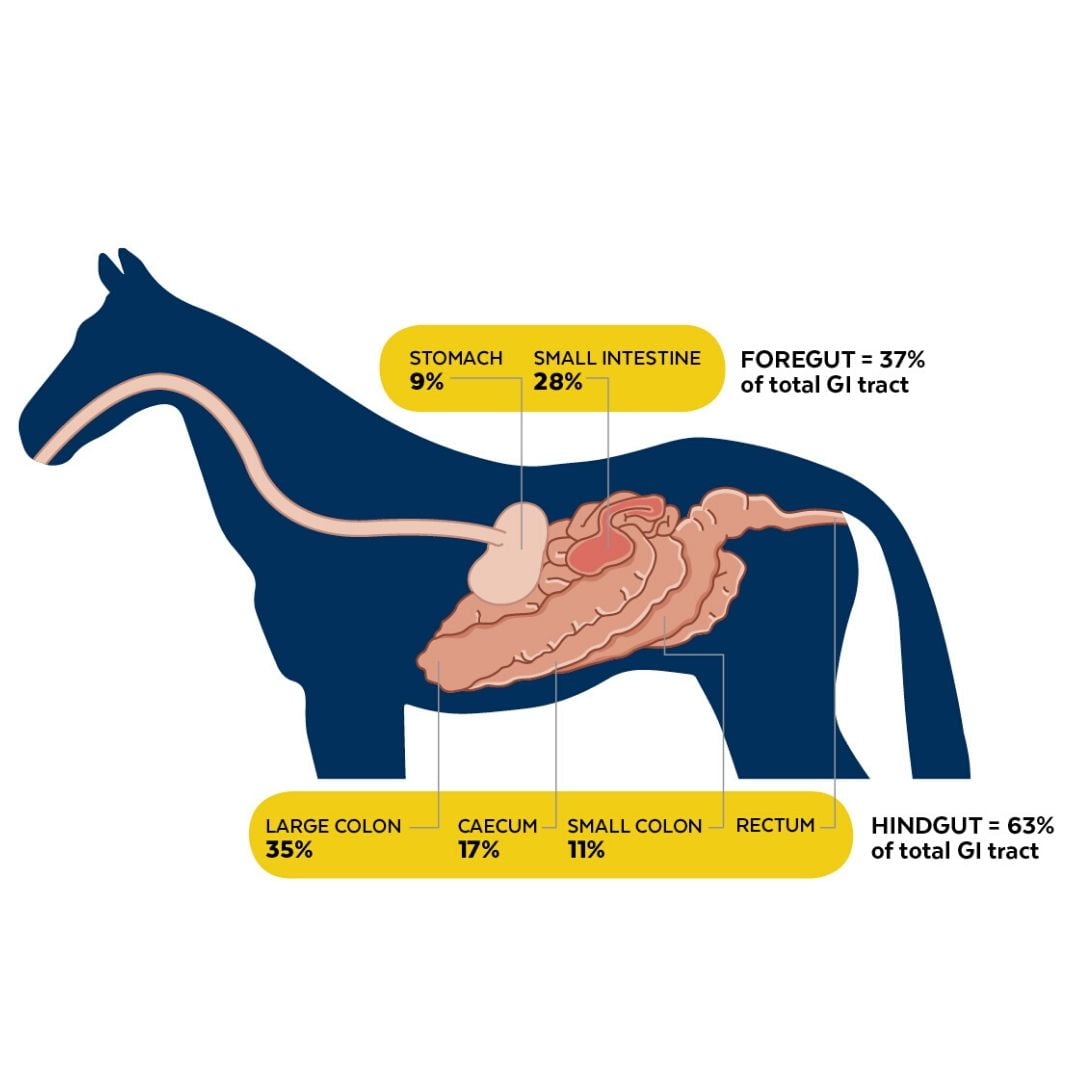
Credit: www.kelato.com.au
Prevention Strategies
Preventing hind gut ulcers in horses requires careful daily care. These ulcers cause pain and affect your horse’s health. Good prevention stops ulcers before they start. Focus on feeding, stable care, health checks, and exercise. These areas help keep your horse’s gut strong and healthy.
Feeding Practices
Feed your horse small amounts often to protect the gut. Use high-fiber forage like hay and grass to support digestion. Avoid too much grain or rich concentrates that can upset the gut. Provide constant access to clean water to keep digestion smooth. Adding probiotics can also help balance gut bacteria.
Stable Management
Keep the stable clean and dry to reduce stress on your horse. Avoid sudden changes in the environment that can upset your horse. Provide comfortable bedding to encourage rest. Reduce dust and ammonia by cleaning stalls daily. A calm, quiet stable lowers stress and supports gut health.
Routine Health Checks
Schedule regular vet visits to catch early signs of ulcers. Watch your horse for changes in behavior or appetite. Check for weight loss or poor coat condition. Early detection allows quick treatment and prevents ulcers from worsening. Keep vaccination and deworming up to date to support overall health.
Exercise Planning
Exercise helps maintain a healthy digestive system. Avoid sudden intense workouts that stress the horse’s body. Plan regular, moderate exercise to improve blood flow to the gut. Rest days allow healing and reduce ulcer risks. Exercise reduces stress, which can trigger ulcers.
Long-term Care
Long-term care for hind gut ulcers in horses is essential for full recovery and lasting health. It involves ongoing attention and smart management. Patience and consistency help your horse heal and stay healthy.
Monitoring Recovery
Watch your horse closely every day. Check for changes in appetite, behavior, or energy. Take notes on any signs of discomfort or improvement. Regular vet visits can track healing progress. Early detection of problems speeds up care.
Maintaining Gut Health
Feed a balanced diet rich in fiber. Avoid sudden changes in feed or routine. Provide constant access to clean water. Use supplements that support digestion and gut lining. Keep stress low by offering a calm environment.
Adjusting Treatment Plans
Treatment may need changes based on healing signs. Follow your vet’s advice carefully. Modify medication or feeding schedules if needed. Be flexible but consistent with care routines. Good communication with your vet ensures the best results.
Recognizing Recurrence
Know the signs of returning ulcers. Watch for poor appetite, weight loss, or colic signs. Act quickly if symptoms come back. Early action prevents severe problems. Staying alert protects your horse’s long-term health.

Credit: madbarn.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Hind Gut Ulcers In Horses?
Hind gut ulcers happen from stress, poor diet, or long use of painkillers.
What Are Common Signs Of Hind Gut Ulcers In Horses?
Look for weight loss, bad mood, poor appetite, and changes in poop.
How Are Hind Gut Ulcers Diagnosed In Horses?
Vets use exams, blood tests, and sometimes special scopes to see ulcers.
Can Diet Help Prevent Hind Gut Ulcers In Horses?
Yes, feeding high-fiber, low-starch foods supports gut health and lowers ulcer risk.
What Treatments Are Available For Hind Gut Ulcers In Horses?
Treatment includes medicines to heal ulcers and improving the horse’s diet.
How Long Does It Take For Hind Gut Ulcers To Heal?
Healing usually takes a few weeks with proper care and treatment.
Conclusion
Hind gut ulcers cause pain and discomfort in horses. Early signs help catch the problem fast. Treating ulcers improves your horse’s health and mood. Good diet and care reduce ulcer risks. Watch your horse’s behavior for any changes. Regular vet check-ups keep ulcers in check.
Healthy horses perform better and feel happier. Keep learning about horse health for their well-being. Small steps make a big difference in prevention. Your horse deserves careful attention and love every day.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.


