As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
If you’re thinking about getting your dog spayed, one question probably stands out: how long does the procedure actually take? You want to know what to expect so you can plan your day and feel prepared.
Understanding the time involved can ease your worries and help you support your furry friend before, during, and after surgery. Keep reading to find out exactly how long the spay takes, what happens during the process, and why this little time investment makes a big difference for your dog’s health.
Credit: healthtimes.co.zw
Procedure Duration
Understanding the time it takes to spay a dog helps pet owners prepare better. The procedure duration varies but is usually short. Knowing what affects the timing gives clear expectations.
The process includes more than just the surgery. Preparation and recovery also add to the total time at the vet.
Typical Surgery Time
The actual spay surgery usually lasts between 20 to 45 minutes. Small dogs often take less time than larger breeds. The vet removes the ovaries and uterus carefully. The surgery is done under general anesthesia to keep the dog still and pain-free.
Factors Affecting Length
Several things can change how long the surgery lasts. The dog’s size and age matter a lot. Older or heavier dogs might need more time. The vet’s experience also affects the speed. Sometimes, unexpected issues inside the abdomen can extend the surgery. The type of spay method used plays a role too.
Pre-surgery Preparation
Before surgery, the vet checks the dog’s health. Blood tests and physical exams ensure safety. The dog must fast for several hours to prevent problems during anesthesia. Preparing the dog properly helps the surgery go smoothly and quickly.
Recovery Timeline
Understanding the recovery timeline after a dog spay helps pet owners prepare better. Recovery varies but usually follows a clear path. Knowing what to expect eases stress for both you and your dog.
Immediate Post-op Care
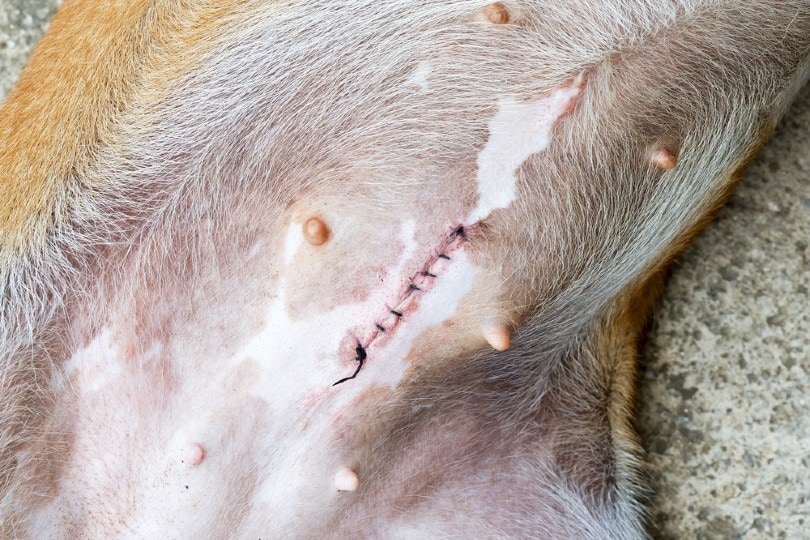
Right after surgery, your dog feels tired and may be groggy. Keep her warm and quiet for the first 24 hours. Offer small amounts of water but wait to feed until she is fully awake. Watch for any bleeding or swelling around the incision. Avoid letting your dog lick or scratch the area.
Healing Stages
The first week is the most crucial for healing. The incision will start to close, and swelling should reduce. Limit your dog’s activity to prevent strain on stitches. By two weeks, most dogs feel much better and can resume light play. Full healing takes about four to six weeks. At this point, the scar is less visible and the skin is strong again.
Signs Of Complications
Watch closely for signs that need vet attention. Excessive redness, swelling, or pus around the wound signals infection. If your dog is vomiting, has diarrhea, or stops eating, call your vet. Difficulty breathing or severe lethargy also require immediate care. Early detection helps avoid serious problems.
Anesthesia Effects
Understanding anesthesia effects is important for dog spaying. Anesthesia helps your dog stay calm and pain-free during surgery. It also means your dog will be unconscious. Knowing what happens during this time can ease your worries.
Anesthesia Duration
Anesthesia usually lasts about one to two hours. This covers the entire spaying procedure. The vet chooses the right type and amount of medicine. It depends on your dog’s size and health. This careful planning keeps your dog safe.
Waking Up Process
After surgery, your dog will slowly wake up. The vet stops giving anesthesia medicine. Your dog may feel sleepy or groggy for a while. Some dogs may shake or cough lightly. This is normal and shows the medicine is wearing off.
Monitoring During Surgery
The vet watches your dog closely during the operation. They check heart rate, breathing, and temperature. Machines help keep track of these signs. This monitoring helps avoid problems during surgery. It ensures your dog stays stable and safe.

Credit: www.arloren.com
Age And Size Impact
Age and size greatly affect the duration of a dog spay surgery. Different dogs need different care and time in the operation room. These factors help the veterinarian plan the best approach for the surgery. Understanding how age and size impact the spay time helps pet owners prepare better.
Small Vs. Large Dogs
Small dogs usually have shorter spay surgeries. Their smaller size means less tissue to work on. Vets can complete the procedure faster and with less anesthesia. Large dogs need more time. They have bigger organs and more body mass. This makes the surgery last longer and the recovery slower. The size difference changes the total time from start to finish.
Puppy Spay Timing
Puppies often have quicker spay surgeries. Their bodies heal faster and are more flexible. Vets find it easier to operate on young dogs. Younger dogs also handle anesthesia better. The whole process takes less time than with adult dogs. Timing the spay early can reduce risks and speed up recovery.
Older Dogs Considerations
Spaying older dogs takes longer than with younger ones. Age brings changes in health and body function. Older dogs may have other health problems. Vets must be careful and use more tests before surgery. The surgery itself may take extra time to avoid complications. Recovery for older dogs also requires more attention and care.
Veterinary Practices
Veterinary practices play a key role in the spaying process. They affect how long the surgery takes and how smoothly it goes. Different factors in the clinic or hospital impact the dog’s care and recovery time.
Clinic Vs. Hospital Settings
Clinics often handle routine spay surgeries. They are smaller and may have less staff. Surgery time can be shorter due to fewer distractions. Hospitals have more resources and specialized equipment. They can manage complex cases and emergencies better. Hospital settings might take longer but offer thorough care.
Surgeon Experience
Experienced surgeons perform spay surgeries faster and with fewer risks. They know how to avoid complications and reduce surgery time. Less experienced vets may take more time to ensure safety. The skill level of the surgeon directly affects the procedure’s length.
Use Of Technology
Modern technology speeds up spay surgeries. Tools like laser scalpels can reduce bleeding and pain. Advanced monitoring devices help track the dog’s condition closely. Technology allows vets to work more precisely and quickly. This leads to shorter surgery times and better outcomes.
Credit: www.whole-dog-journal.com
Post-surgery Tips
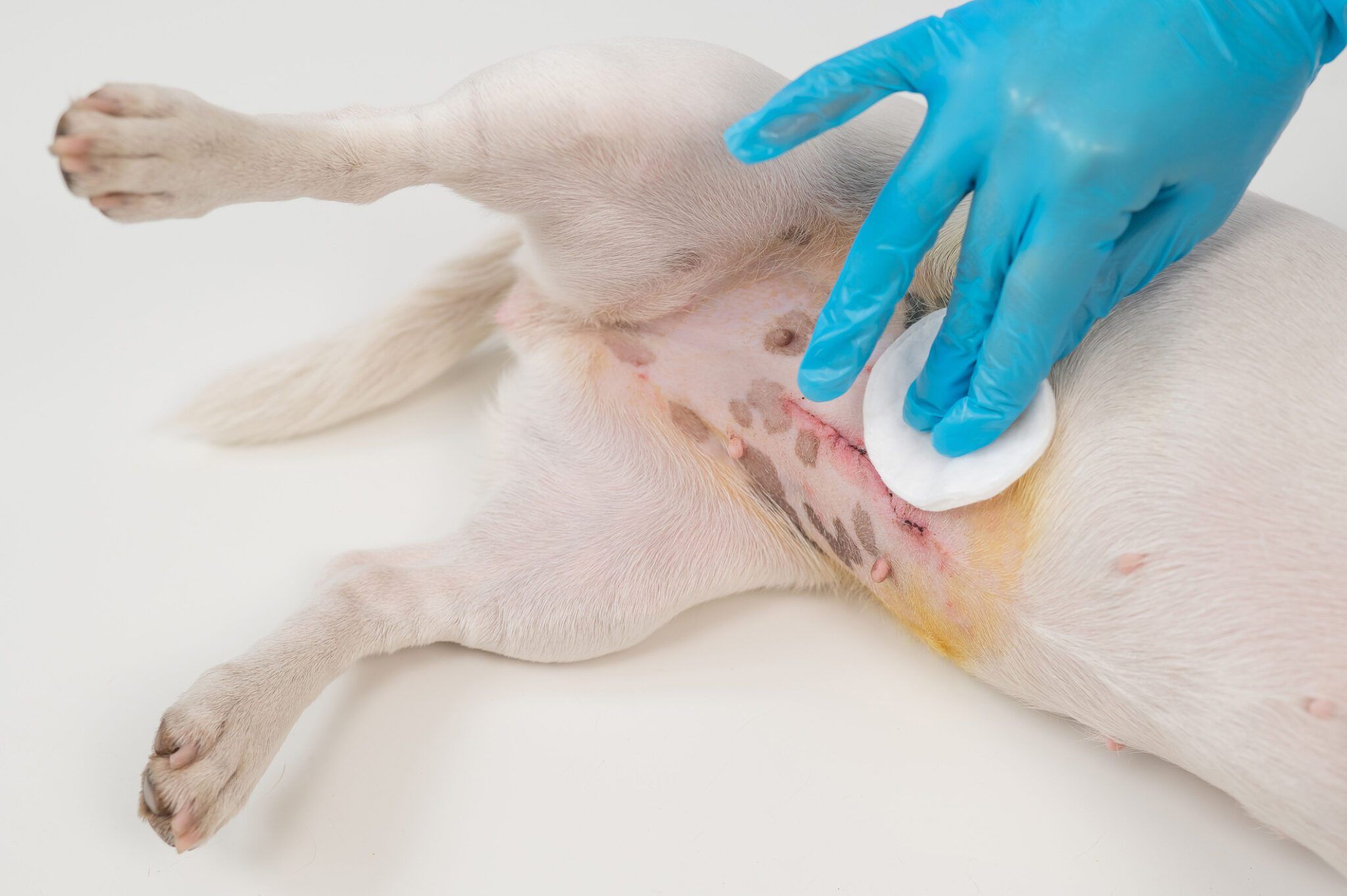
After your dog’s spay surgery, proper care helps her heal faster. Following clear post-surgery tips keeps your dog safe and comfortable. These tips cover home care, activity limits, and feeding. Each step supports recovery and prevents problems.
Home Care Instructions
Keep your dog’s rest area quiet and clean. Check the incision daily for redness or swelling. Stop your dog from licking or biting the stitches. Use an Elizabethan collar if needed. Give all medicines exactly as the vet says. Never skip doses or change amounts.
Activity Restrictions
Limit your dog’s movement for at least two weeks. Avoid running, jumping, or playing hard. Short leash walks are best for bathroom breaks. Too much activity can open the wound or cause pain. Watch your dog closely and stop rough behavior early.
Nutrition And Hydration
Offer fresh water at all times to prevent dehydration. Feed a light, balanced diet for the first few days. Smaller meals can help avoid nausea after surgery. Do not change food suddenly during recovery. Follow your vet’s advice on when to return to normal feeding.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does The Spay Surgery Usually Take?
Spay surgery typically takes 20 to 45 minutes, depending on the dog’s size and health.
How Long Does It Take For A Dog To Recover?
Most dogs recover within 10 to 14 days after spaying surgery.
What Happens During The Dog Spay Procedure?
The vet removes the ovaries and uterus to prevent pregnancy in the dog.
Is My Dog Awake During The Spay Surgery?
No, dogs are under general anesthesia and do not feel pain during surgery.
How Soon Can My Dog Go Home After Spaying?
Dogs usually go home the same day, once they wake up from anesthesia.
When Can My Dog Resume Normal Activities After Spaying?
Limit activity for about two weeks to allow proper healing after spay surgery.
Conclusion
A dog spay usually takes about 30 to 60 minutes. The time depends on the dog’s size and health. Recovery starts soon after surgery. Most dogs feel better within a few days. Keep your dog calm and follow the vet’s advice.
Watch for any signs of trouble, like swelling or lack of appetite. Spaying helps prevent health problems and unwanted puppies. Knowing how long the surgery takes can ease your worries. Your pet will be healthier and happier in the long run.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

