As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
A cat has one jaw. This jaw consists of two parts: the upper and lower jaws.
Cats are fascinating creatures. Their anatomy is both unique and complex. Understanding how many jaws a cat has can help in knowing more about their behavior and health. While it might seem simple, the structure of a cat’s jaw plays a key role in their daily life.
From eating to playing, their jaw is always at work. In this post, we will explore the anatomy of a cat’s jaw. We will also discuss its function and importance. Stay with us as we dive into the intriguing world of feline anatomy.
Introduction To Feline Anatomy
Understanding a cat’s anatomy can be intriguing and insightful. Cats possess unique physical traits that make them fascinating creatures. This post delves into the anatomy of cats, focusing on their jaws.
Fascination With Cats
Cats have captivated humans for centuries. Their agility and mysterious nature intrigue us. People often marvel at their grace and stealth. These qualities stem from their unique anatomical structure.
Importance Of Studying Cat Anatomy
Studying cat anatomy helps us understand their behavior. It aids in providing better care for our feline friends. Knowing their anatomy can also assist in detecting health issues early.
Cat jaws play a crucial role in their daily activities. From eating to grooming, their jaws are essential. Cats have two jaws, upper and lower. These jaws are equipped with sharp teeth, designed for cutting and tearing.
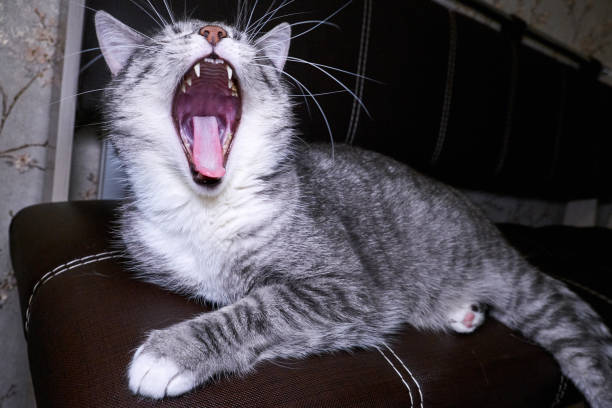

Credit: www.istockphoto.com
Basic Structure Of A Cat’s Skull
The basic structure of a cat’s skull is fascinating. It protects the brain and supports the jaws. Understanding the skull can help us care for our pets better. Let’s explore its components and functions.
Components Of The Skull
The cat’s skull has several key parts. The cranium protects the brain. The jawbones are the mandible and maxilla. The mandible is the lower jaw. The maxilla forms the upper jaw. The zygomatic arches give strength to the face. The nasal bones support the nose. Each part plays a vital role.
Functions Of The Skull
The skull has important functions. It protects the brain from injury. It supports the jaws for eating. The jawbones help in chewing food. The nasal bones help in breathing. The skull also provides attachment points for muscles. These muscles assist in movement and expressions. All these functions ensure a cat’s survival.
Jaw Anatomy In Cats
Cats have a unique jaw structure that plays a crucial role in their daily lives. Understanding the anatomy of their jaws helps us appreciate their eating habits and behaviors. Let’s dive into the details of the upper and lower jaw structures in cats.
Upper Jaw Structure
The upper jaw in cats is known as the maxilla. It is a fixed part of the skull and does not move. The maxilla holds the upper teeth in place. These teeth include the incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
- Incisors: Small front teeth used for grooming and biting.
- Canines: Long, sharp teeth for catching and holding prey.
- Premolars: Teeth behind canines for tearing food.
- Molars: Back teeth for grinding food.
The upper jaw also contains the nasal passage. It supports the structure of the cat’s nose.
Lower Jaw Structure
The lower jaw is called the mandible. Unlike the upper jaw, the mandible is movable. It allows cats to open and close their mouths. This movement is essential for eating and vocalizing.
The mandible also holds teeth similar to the upper jaw:
- Incisors: For grooming and small bites.
- Canines: For gripping and tearing.
- Premolars: For tearing food.
- Molars: For grinding.
Between the two jaws, a powerful set of muscles controls movement. These muscles help cats bite and chew their food efficiently.
Understanding the jaw anatomy of cats helps us better care for their dental health. Regular check-ups and proper nutrition are vital for maintaining healthy jaws and teeth.
How Cats Use Their Jaws
Cats have fascinating anatomy. Their jaws are especially interesting. Not only do these jaws help in eating, but they also play vital roles in hunting and catching prey.
Eating And Chewing
Cats have sharp teeth designed for cutting food. Their jaws move up and down, not side to side. This movement makes chewing easier. Cats do not grind their food. Instead, they tear it into smaller pieces. This method ensures quick and efficient eating.
Hunting And Catching Prey
A cat’s jaws are crucial for hunting. They help catch and hold prey tightly. The sharp teeth penetrate the prey’s skin. This ability is essential for survival in the wild. Even domestic cats display hunting behaviors. They catch mice or toys with their jaws. This instinct is deeply embedded in their nature.
Teeth And Their Role
Cats have one jaw. Their teeth help them chew food and catch prey. Cats use their sharp teeth to tear meat.
Cats have fascinating teeth. Their teeth are essential for many reasons. They help cats eat and defend themselves. Cats have different types of teeth, each with a specific function.Types Of Teeth
Cats have four types of teeth. These include incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Each type has a unique role in a cat’s life.Functions Of Different Teeth
Incisors are small but sharp. They help cats groom and pick up food. Canines are long and pointed. Cats use them to catch and kill prey. Premolars and molars help in chewing food. They break down the food into smaller pieces for easy swallowing. “`
Credit: www.nhm.ac.uk
Comparing Cat Jaws To Other Animals
Understanding the anatomy of a cat’s jaws can be fascinating. Cats have unique jaw structures, which differ significantly from other animals like dogs and humans. Let’s explore these differences to appreciate how special our feline friends truly are.
Differences From Dogs
Cat jaws are designed for cutting and tearing meat. They have fewer teeth than dogs, with 30 teeth compared to a dog’s 42. Cats have sharp, pointed teeth, while dogs have a mix of sharp and flat teeth. This is because dogs are omnivores, and their diet includes plants.
Cat jaws move only up and down. This helps them bite down hard on their prey. Dogs have jaws that can move side to side. This lets them grind their food. Cats’ jaws also lock in place when they bite, giving them a strong grip.
Differences From Humans
Humans have 32 teeth, similar to cats in number. But our teeth serve different purposes. Human teeth are flat and ideal for grinding and chewing. We also have a mix of incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Cats, on the other hand, have specialized teeth for hunting.
Human jaws can move in multiple directions. This allows us to chew food thoroughly. Cat jaws, however, only move up and down. This helps them focus on tearing meat. Another difference is the presence of the temporomandibular joint in humans. This joint lets us move our jaws in complex ways.
In summary, a cat’s jaws are uniquely adapted for their predatory lifestyle. Their jaw structure allows them to efficiently catch and consume prey.
Common Jaw-related Health Issues
Cats, like humans, can face various jaw-related health problems. These issues can affect their eating habits, cause pain, and lead to other health problems. This section will explore common jaw-related health issues in cats.
Dental Problems
Cats often suffer from dental problems. Tooth decay and gingivitis are common. These issues can cause severe pain and discomfort.
- Tooth Decay: Plaque and tartar build-up can lead to cavities.
- Gingivitis: Inflammation of the gums can make eating painful.
Regular dental check-ups are crucial. They help to prevent these problems. Dental cleanings and good oral hygiene can keep your cat’s mouth healthy.
Injuries And Fractures
Cats are active animals. They can easily injure their jaws. Falls and fights with other animals are common causes.
| Type of Injury | Common Causes |
|---|---|
| Fractures | Falls from high places, car accidents |
| Dislocations | Fights with other animals, rough play |
Signs of jaw injuries include swelling, drooling, and difficulty eating. If you notice these signs, visit a vet immediately.
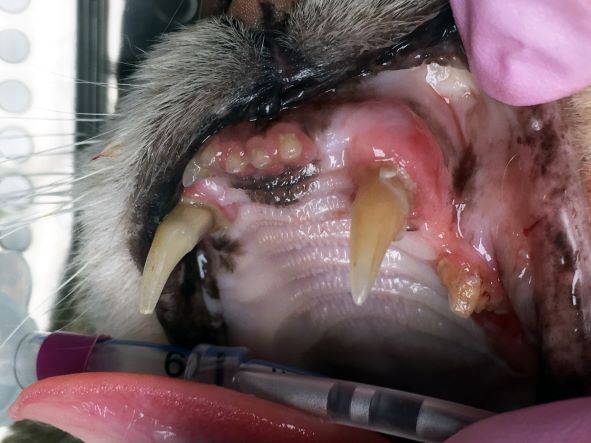
Credit: www.rvc.ac.uk
Caring For Your Cat’s Jaw Health
Keeping your cat’s jaw healthy is essential for their overall well-being. Cats use their jaws for eating, grooming, and playing. Any issues with their jaw can lead to discomfort and health problems. Here are some key ways to care for your cat’s jaw health.
Regular Check-ups
Take your cat to the vet for regular check-ups. The vet can spot early signs of jaw problems. They will check for broken teeth, gum disease, and other issues. Early detection helps prevent serious conditions. Make sure to schedule these visits at least once a year.
Proper Nutrition And Dental Care
Feed your cat a balanced diet. Good nutrition supports strong bones and teeth. Dry food can help reduce plaque buildup. Provide your cat with dental treats to clean their teeth. Regular brushing also plays a crucial role. Use a cat-specific toothbrush and toothpaste. These steps help maintain good jaw health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Jaws Does A Cat Have?
A cat has one jaw, which consists of two parts: the upper jaw (maxilla) and the lower jaw (mandible).
What Is The Function Of A Cat’s Jaw?
A cat’s jaw helps in chewing food, grooming, and biting. It also aids in vocalizing and communicating.
Do Cats Have Strong Jaws?
Yes, cats have strong jaws. Their jaw muscles are powerful, enabling them to catch and eat prey efficiently.
How Does A Cat’s Jaw Differ From A Human’s?
A cat’s jaw differs from a human’s in shape and function. It is designed for hunting and eating meat.
Conclusion
Cats have only one jaw, just like humans. Their jaw structure is unique. It allows them to catch and chew food efficiently. Understanding this helps us appreciate our feline friends more. Knowing these details can improve our care for them.
Always remember, a healthy jaw means a happy cat. Keep your cat’s dental health in check. Regular vet visits are important. Now, you know more about your cat’s jaw. Share this knowledge with other cat lovers. Your cat will thank you!
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.